基于 南科大 于仕琪老师的课程学习笔记
【快速学习C和C++,基础语法和优化策略,学了不再怕指针(南科大计算机系原版)】https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Vf4y1P7pq?vd_source=5a0790755035f26a67935abfbfcdfd5b
推荐文章
C++ 如何进阶?如何准备 C++ 面试? - 知乎
程序基本常识
编译与链接
C语言编译原理涉及将C语言代码转换为机器语言的过程。这个过程包括预处理、编译、汇编和链接。编译器在这个过程中对源代码进行优化和转换,生成可执行文件,主要包括以下几个阶段:
1. 预处理(Preprocessing)
作用:处理源代码文件中的预处理指令,如#include和#define
过程:替换宏定义,处理条件编译指令,包含头文件内容
工具:预处理器,如cpp、armclang
2.编译(Compilation)
作用:将预处理后的源代码转换成汇编语言
过程:进行语法分析和语义分析,生成汇编代码
工具:编译器,如GCC、armclang
3.汇编(Assembly)
作用:将汇编语言转换成机器语言,即目标代码(Object Code)
过程:汇编器将汇编指令转换为机器码
工具:汇编器,如as、armasm
4.链接(Linking)
作用:将多个目标代码文件和库文件合并成一个单独的可执行文件
过程:
解决外部符号引用,如函数和全局变量
合并不同模块中的相同段(如.text,.data)
生成最终的可执行文件或库文件
工具:链接器,如ld、armlink
编译器与链接器
在整个编译过程中,编译器和链接器是核心组件,一般的环境配置也主要针对这二者展开:
编译器(Compiler):负责将源代码转换成汇编代码或直接生成目标代码。编译器的高级优化包括循环优化、常数传播、死码删除等
链接器(Linker):负责将多个目标代码文件整合为一个可执行文件。链接器处理符号解析、重定位等任务
错误
编译错误,链接错误,运行错误
预处理与宏
预处理,对宏定义进行替换
宏就是字符替换
初始化
c++11开始支持的初始化{}和()
1
2
3
4
|
int test{};//初始化为0,c++11支持,c++98不支持
int man();//初始化为0,c++11支持,c++98不支持
int wow[]{1,2,3};//初始化,c++11支持,c++98不支持
int test_man[] = {0,1,2};//初始化,c++11支持,c++98支持
|
Data-Types-and-Arithmetic-Operators
integer-numbers
int
注意在不同平台上,int,short int,long int,long long的定义是不同的
sizeof()
sizeof是一个操作符,不是函数
1
2
3
|
int i ;
cout << sizeof(int) << endl ;
cout << sizeof(i) << endl ;
|
char
char本质上是一个8位的整数,可以用有符合和无符号修饰符修饰
1
2
3
|
char CH ;
unsigned char UCH ;
signed SCH ;
|
注意char在不同平台上不一定是signed char,有可能是unsigned char
一般char是int8_t
bool
bool数据类型,1byte而不是1bit,同时这是c++里的数据类型
c语言中需要#include <stdbool.h>来引入bool数据类型,或者有以下代码来使用bool
1
2
3
|
typedef char bool;
#define true 1
#define false 0
|
注意给bool类型数据赋值,只要不是0,就都是1
1
2
|
bool test = -256 ;
cout << test ;
|
输出test,会发现test是1
cstdint
c++11之后引入<ctsdint>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
int8_t
int16_t
int32_t
int64_t
uint8_t
uint16_t
uint32_t
uint64_t
|
以及一些宏
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
INT8_MIN
INT16_MIN
INT32_MIN
INT64_MIN
INT8_MAX
INT16_MAX
INT32_MAX
INT64_MAX
|
floating-point-numbers
float
单精度浮点数,float类型的数据一定会带有误差
32bits
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
int main() {
float f1 = 1.2f ;
float f2 = f1*1000000000000000 ;//1e15
cout << std::fixed<<std::steprecision(15)<< f1 << endl ;
cout << std::fixed<<std::steprecision(15)<< f2 << endl ;
return 0 ;
}
|
输出结果
1
2
|
1.200000047683716
1200000038076416.000000000000000
|
float类型数的规格,详见IEEE规定
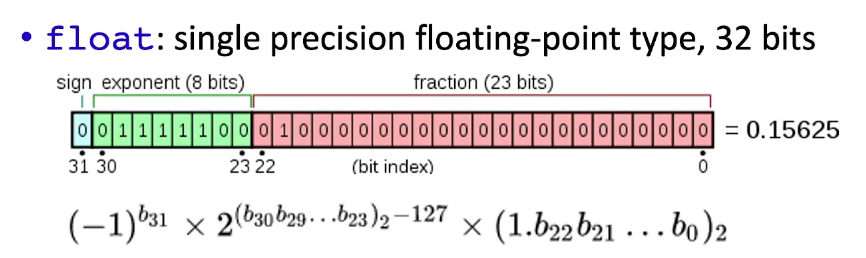
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
int main() {
float f1 = 2.34E+10f;
float f2 = f1+10;//but f2=f1
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed,ios_base::floatfield);//fixed-point
cout << "f1=" << f1 << endl;
cout << "f2=" << f2 << endl;
cout << "f1-f2" << f1-f2 <<endl;
cout << "(f1-f2==0)="<<(f1-f2==0) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
输出结果
1
2
3
4
|
f1=23399999488.000000
f2=23399999488.000000
f1-f2=0.000000
(f1-f2==0)=1
|
原因是float类型本质是在采样点,该例子中中+10的采样点间隔不够,数值不发生变化
浮点数是取一些间隔值
关于.f/.F
在 C++ 中,1.0f 和 1.0F 都表示单精度浮点数(float 类型),两者在功能上是完全等价的,唯一的区别是字母 f 的大小写不同。
说明:
1.0f 和 1.0F 都表示 float 类型的字面量,值为 1.0。- 如果不加后缀
f 或 F,例如 1.0,则默认是 double 类型(双精度浮点数)。
- 类似地,
1.0L 或 1.0l 表示 long double 类型(扩展精度浮点数)。
示例:
1
2
3
4
|
float a = 1.0f; // float 类型
float b = 1.0F; // 同上,float 类型
double c = 1.0; // double 类型
long double d = 1.0L; // long double 类型
|
为什么有两种写法?
C++ 允许 f 和 F 两种写法,主要是为了代码风格的一致性。例如:
- 某些编码规范可能推荐使用大写
F 以增强可读性(避免与数字 1 混淆)。
- 而小写
f 更常见,因为更简洁。
总结:
1.0f 和 1.0F 在 C++ 中完全等价,选择哪一种取决于个人或团队的代码风格偏好。
浮点数不要直接相等
浮点数都是近似,不是精确的数值,所以不适合用==判断相等
1
2
|
if(f1==f2)//bad
if(fabs(f1-f2)<FLT_EPSILON)//good
|
inf and nan
1
2
|
float f1 = 2.0f / 0.0f ;
float f2 = 0.0f / 0.0f ;
|
+/- inf:infinity ( Exponent=11111111 , fraction=0 )
nan:not a number ( Exponent=11111111 , fraction!=0 )
如果计算过程中出现了inf或者nan,后续的计算会产生问题
double
双精度浮点数,64bits
long double
如果系统支持,128bits
否则,64bits
Arithmetic Operators
算数运算,对计算的实现要有所理解,才能避免出现一些错误
Constant-numbers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
95//十进制
0137//八进制
0x5F//十六进制
95//int
95u//unsigned int
95l//long
95lu//unsianed long
95ul//unsianed long
3.14//3.14
6.02e23//6.02*10^23
1.6e-19//1.6*10^-19
6.02e23L//long double
6.02e23f//float
6.02e23//double
|
const类型限定符
在变量前加了const限定符,变量的值就不可以被修改了
1
2
|
const float PI = 3.1415926f ;
PI += 1 ;//error!
|
运算符优先级
1
2
3
4
5
|
a++
++a
* /
+ -
<< >>
|
赋值操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
a = b
a += b
a -= b
a *= b
a &= b
a |= b
a <<= b
a >>= b
|
自增自减
1
2
3
4
|
i ++
++ i
i --
-- i
|
1
2
3
|
int i = 3 ;
int b = i ++ ;//先赋值再++
int c = ++ i ;//先++再赋值
|
类型转换
浮点类型转整型,会直接舍弃小数位,保留整数位
1
2
|
implicit conversion 隐式转换
explicit conversion 显式转换
|
很多时候有错的隐式转换不会被报错,能正常编译,需要格外注意
1
2
3
|
float f = 17 / 5 ;//f will be 3.f , not 3.4f
float f = 17 / 5.f ;//f will be 3.4f
|
除法两边都是整数,做的是整数除法
Data loss
占用字节低的数据类型 转换到 占用字节高的数据类型,不会有数据丢失
占用字节高的数据类型 转换到 占用字节低的数据类型,就会有数据丢失
Auto
auto( since C++11 )
auto is placeholder type specifier
1
2
3
|
auto a = 2;//type of a is int
auto b - 2.3;//type of b is double
auto c ;//valid in C , error in C++
|
auto在初始化阶段就会确定数据类型,后面不再改变
1
2
|
auto a = 2;
a = 2.3 ;// int = 2.3 , 会发生类型转换,最后a = 2
|
Branching-and-Looping-Statements
循环和分支结构
if else
如果没有花括号去约束,else会与最近的if配对
三目运算符
1
2
3
|
factor = isPositive ? 1 : -1 ;
//isPositive成立,取前面的值
//isPositive不成立,取后面的值
|
Logical Expressions
!>&&>||
如果逻辑运算两边不是布尔,则会隐式转换为布尔
1
2
|
if( -2 && true )//-2会被强制转换为bool,其布尔值为1(只要不是零,全部转换成1)
cout << "The condition is true." << endl;
|
指针用作条件判断时
1
2
3
|
int * p = new int [1024];
if(!p)// if( p == NULL )
cout << "Memory allocation failed." << endl ;
|
while loop
如果条件为true,就会执行循环
循环执行中间可以用break打断循环,或者用continue跳过当前循环
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
size_t num = 10 ;
while( num >= 0 ) {
cout << "num = " << num << endl ;
num -- ;
}
//这是一个死循环,size_t是无符号数
|
赋值操作这个表达式也有值
1
2
3
4
|
bool flag = false ;
while( flag = true ) {
flag = false ;
}
|
do-while loop
先执行一次循环,再判断条件
for loop
1
2
|
for(init-clause;cond-expression;iteration-expression)
loop-statement
|
初始化表达式,条件表达式,迭代表达式
endless-loop
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
for(;;) {
}
while(true) {
}
|
goto-and-switch Statement
case相当于goto的label
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
switch(str) {
case 'a':
break;
case 'b':
break;
default:
break;
}
|
Data-Structures
Array
在C和C++中,数组就是一块连续的内存
数组的名字指向数组的首地址
初始化
1
2
|
int number[5]={2,2};//只初始化前两个值
int number[5]{2,2};
|
需要注意数组操作没有越界提示,甚至可以取负数
但如果超出应用程序的内存边界时,会被操作系统杀死
变长数组
其长度由变量决定,在运行时决定而非编译时决定
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
int len = 0 ;
int num_array[len];//可以为0
for (int i = 1 ; i < 10 ; ++ i ) {
cout << sizeof(num_array) << endl ;
++ len ;
}
|
Array of unkown size
未知长度的数组
1
2
3
4
5
|
int num_array[]={1,2,3,4};
//作为函数参数
float array_sum(float values[],size_t length);
float array_sum(float *values,size_t length);
|
二维数组
1
2
3
|
void init_2d_array(float mat[][] , uint8_t rows , uint8_t cols);//error
void init_2d_array(float mat[][3] , uint8_t rows , uint8_t cols);
|
const-Arrays
const修饰的数组不允许被修改
Strings
Array-style strings
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
char man[4]={'m','a','n'};
char MAN[3]={'M','A','N'};//a bad one
char Man[4]={'M','a','n','\0'};
//beter defination
//更好的定义方式
char name[]="MAN!";
//数组大小是5,字符串大小是4
|
strlen(Man)==3,因为有\0限制
string class
同样没有越界检查
1
2
|
#include <string>
std::string str1 = "MAN";
|
Struct&Union&Enum
Struct
注意有内存对齐
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
typedef
struct Student{
char name[4];
int born;
bool male;
}Stu;
struct Student stu={"Yu",2004,true};
Stu stu1 ;
|
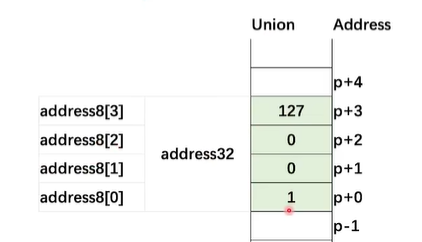
Union
Union所有成员共享一个内存,以最大的成员变量为准
相当于同一个数据多个名字
1
2
3
4
|
union ipv4add{
std::uint32_t add32;
std::uint8_t add8[4];
};
|
Enum
枚举类型
1
2
3
4
|
enum color{WHITE,BLACK,RED,BLUE};(0,1,2,3)
enum color pen_color = RED ;
pen_color += 1;//error
|
typedef
用于创建别名
1
|
typedef unsigned char uint8_t;
|
Memory and Pointer
Pointers
指针变量存储的是一个地址
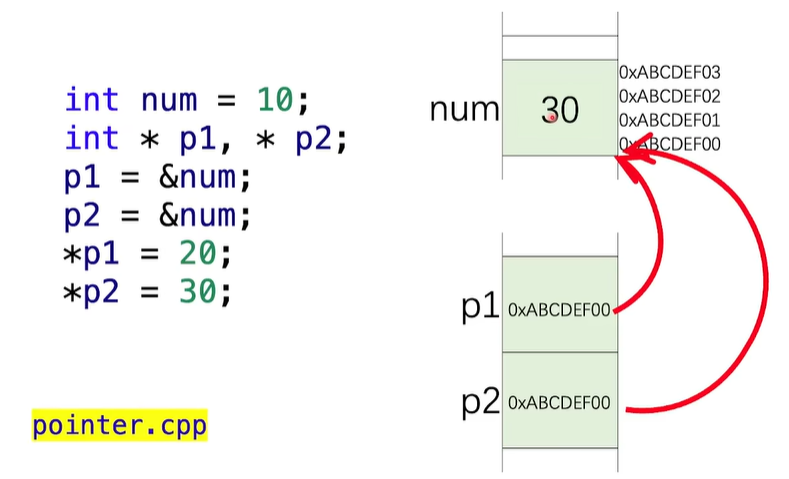
对指针进行加减,加减是加减一个元素
1
2
|
int numbers[4];
int * p =numbers+1 ;//加1个元素,每个元素是4个字节
|
Pointers of Pointers
1
2
3
|
int num=10;
int * p =#
int ** pp = &p ;
|
const pointers
该指针指向的内容不可以通过该指针去修改
1
2
|
*p1 = 3;//error
num=3;//ok
|
可以修改指针指向的内容,但指针不能去指其他值
1
2
3
|
int * const p2 = &num ;
*p2 = 3 ;//ok
p2 = &another;//error
|
换行转义符
虽然实际上是3行,但是在语义上是1行
1
2
3
|
#define PRINT_ARRAY(array,n) \
for( int i = 0 ; i < (n) ; ++ i ) \
cout << (array)[i] << endl;
|
Allocate-memory:C-style
只是示意图,在不同系统下会有区别
 申请内存
申请内存
1
|
int *p1 = (int*)malloc(4);
|
释放内存
内存泄漏问题
第一次申请的内存无法进行管理了,无法回收
1
2
3
4
5
|
p = (int *)malloc(4*sizeof(int));
// ...
p = (int *)malloc(8*sizeof(int));
// ...
free(p);
|
p是局部变量,函数返回后就消失了,这段申请的内存就无法回收了
1
2
3
4
|
void foo() {
int * p = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
return ;
}//memory leak
|
Allocate-memory:C++-style
operator new and new[]
申请内存,比malloc功能更丰富
new是一个操作符
1
2
3
4
5
|
int * p1 = new int ;
int * p2 = new int(5);//申请内存后初始化为5
int * p3 = new int();//初始化为0
int * p4 = new int{};//初始化为0
|
1
2
|
int * pa1 = new int[16]{1,2,3};//申请16个int的内存,64字节
//同时还进行初始化
|
operator delete and delete[]
对于数组和普通变量而言,没有区别
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
int *p1 = new int ;
int *ps1 = new int[16];
delete p1 ;//没区别
delete []p1 ;
delete ps1 ;
delete []ps1;
|
但如果是一个类的对象的数组,两种方式都会释放所有的内存,
但是delete只有第一个元素会去调用析构函数,
delete[]所有元素都会去调用析构函数
1
2
3
4
|
stu *p1 = new stu[3] ;
delete p1 ;
delete []p1 ;
|
Basics of Functions
Functions
函数是为了让编程更加模块化而设计的
Parameters
传参的两种方式,值传递和引用传递
值传递的值可以认为是一个函数内的局部变量
值传递
值传递的值可以认为是一个函数内的局部变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
int foo(int x) {
x += 10 ;
return x ;
}
int main() {
int num1 = 20 ;
int num2 = foo(num1);
return 0;
}
|
x是num1的一份拷贝(会涉及拷贝构造函数)
引用传递-Reference
引用是一个变量的 别名
1
2
|
int num = 0;
int & num_ref = num ;//别名
|
 引用创建的时候一定要初始化
引用创建的时候一定要初始化
在函数传递一个内存占用巨大的参数时,采用值传递,拷贝的变量会占用大量内存,这个时候可以使用指针或者引用
指针与引用的区别
引用相较于指针更加安全
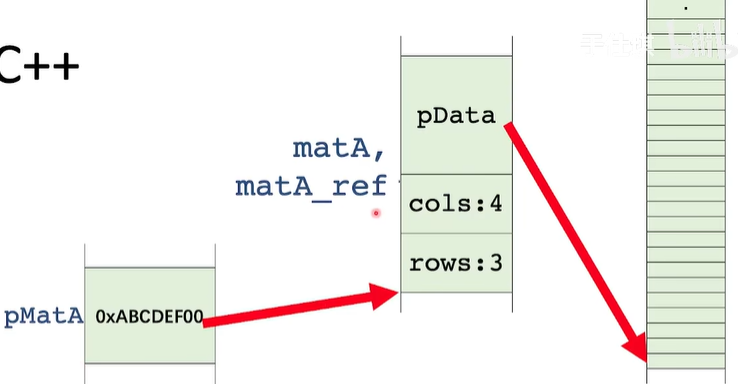
Return-statement
如果return一个数据很大,可以采用以下的方式
1
2
3
4
5
|
bool matrix_add(const Matrix & matA , const Matrix & matB , Matrix & matC ) {
//检查参数是否正常
//...
//return true if everything ok
}
|
Inline-functions
内联函数,众所周知,函数的调用是有代价的,需要将一部分数据压入栈中,跳转执行完后再回来出栈
如果一个微小的函数且被频繁调用,这个代价就会变得不可忽视,此时可以使用内联函数(空间换时间的典型案例)
1
2
3
4
|
inline float max_function(float a ,float b ) {
if(a>b) return a;
else return b;
}
|
需要注意的是inline是建议编译器以内联inline的方式编译这个函数(所以有可能编译器会不听你的建议)
内联函数&宏 的区别
与宏定义是有去别的,宏定义是在预编译之前的文本替换,有较大的安全性问题
注意,宏是在做文本替换,一定要警惕文本替换后的运算符优先级问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
//宏 文本替换后运算优先级
#define MAX_MACRO(a,b) (a)>(b) ? (a):(b)
//#define MAX_MACRO(a,b) a>b ? a : b
int num1=20;
int num2=30;
int maxv=MAX_MACRO(num1,num2);
int maxt=MAX_MACRO(num1++,num2++);
//maxt=(num1++)>(num2++)?(num1++):(num2++);
//实际执行了两次num2++,num2实际是32
//而num1只执行了一次num1++,num1实际是31
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
//宏 文本替换后运算优先级
//#define MAX_MACRO(a,b) (a)>(b) ? (a):(b)
#define MAX_MACRO(a,b) a>b ? a : b
int num1=0xAB09;
int num2=0xEF08;
int maxv=MAX_MACRO(num1&0xFF,num2&0xFF);
//maxv=0x0009
//maxv= num1&0xFF > num2&0xFF ? num1&0xFF : num2&0xFF
//实际上>优先级大于&
//执行的是num1&(0xFF>num2)&0xFF
|
Advances in Functions
Default-arguments
默认参数是C++的特性,C并不支持
1
2
3
|
float norm(float x,float y,float z);
float norm(float x,float y,float z=0);
//x,y,z是parameters,z=0的0是arguments
|
Function-Overloading
函数重载是只有C++才支持的特性,C并不支持
与C++和C函数名符号修饰有关
需要注意的是,C++的函数重载只允许将参数重载,而不能重载返回值
1
2
3
|
float sum(float x , float y);
double sum(float x , float y);//error
//会出现重定义的错误
|
同时要注意,函数调用不要出现歧义,一旦出现歧义,编译器会停止工作,无法编译通过
Function-templates
函数模板生成的函数是模板函数,模板函数是函数模板被实例化以后生成的
此处的T是定义的一个泛型
1
2
3
4
5
|
template<typename T>
T sum(T x , T y ) {
cout << "The input type is"<< typeid(T).name() << endl;
return x+y;
}
|
函数模板定义后,当编译器看到这段代码的时候,编译器并不会去生成真正的可执行代码
要让编译器去生成函数模板对应的可执行代码需要实例化
1
2
3
4
|
template double sum<double>(double,double);//全写
template char sum<>(char,char);//省略<>内的定义
template int sum(int,int);//省略<>
//以上是显示的实例化
|
需要注意的是,函数模板除了显式的实例化,还可以做隐式的实例化
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
template float sum<float>(float,float);//全写
//1.0f (float)
//1.0 (double)
auto man = sum(1.0,1.0);//会进行隐式实例化
//实例化的模板函数应该是
//template double sum<double>(double,double);
|
隐式的实例化可以指定实例化的类型
1
2
|
auto man = sum<int>(1.0f,2.0f);
//这里指定实例化类型后,对参数会有隐式转换
|
实例化后还可以进行自定义,也就是特例化,特例化的代码是会被编译的,一般会放在.cpp源文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
//Point是一个结构体
//注意template后面一定要加<>
template <>
Point sum<Point>(Point pt1,Point pt2) {
cout << "The input type is " << typeid(pt1).name() << endl ;
Point pt;
pt.x = pt1.x+pt2.x;
pt.y = pt1.y+pt2.y;
}
|
Function-Pointers and References
Function-Pointers
函数指针是一个指针,指向函数,也就是指向执行指令的地址
指针函数的类型需要与其指向的函数类型完全匹配
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
float nprm_l1(float x , float y);
float norm_l2(float x , float y);
float (*norm_ptr)(float x , float y);//括号不能省
//两种写法等价
norm_ptr = norm_l1;
norm_ptr = &norm_l2;
float len1 = norm_ptr(-3.0f,4.0f);
float len2 = (*norm_ptr)(-3.0f,4.0f);
|
常见的应用案例是将函数作为一个参数传递到另外一个函数里面,作为回调函数
Function-references
函数引用,需要注意函数引用在初始化的时候需要定死
1
2
3
|
float nprm_l1(float x , float y);
float norm_l2(float x , float y);
float (&norm_ref)(float x, float y) =norm_l1;
|
Recursive-Functions
递归函数,自己调用自己,需要有递归终止条件,否则一直递归会爆栈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
void div2(double val) {
if(val>1.0) {
cout << val << endl;
div(val/2);
}
else cout << "over";
cout << val << endl;
}
|
函数的每一次调用需要压栈进行数据保存,无穷递归就会导致爆栈
Speedup-Your-Program
C-and-Cpp-with-arm
C和C++语言是由明确的语言规范的,是具有平台无关性的,能通过编译器编译成平台相关的可执行程序
机器人或者说是智能设备领域全是arm的天下
Speedup-Your-Program
Simple is Beautiful
代码优化常用策略上,优化代码一定要考虑到内存
- 大量的内存读写带来的时间浪费
- 非连续内存的跳跃式读取导致的
cache命中率下降
- 避免大量的内存拷贝
关于
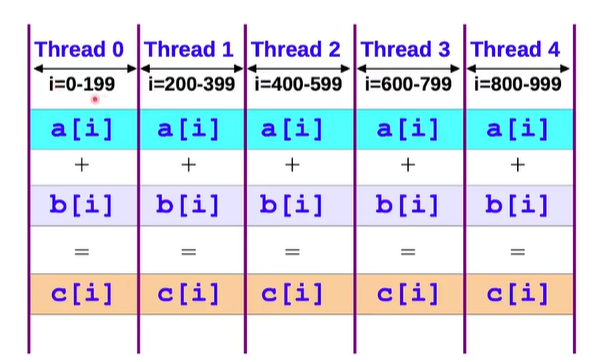
SIMD和OpenMP
SIMD:Single instruction,multiple data (例如向量加法)
OpenMP
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
#include <omp.h>
#pragma omp parallel for
for( int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i )
c[i] = a[i]+b[i];
//将循环拆开,分给不同的cpu核运行
//需要注意将任务拆开给不同的cpu核本身也是需要时耗的
|
Basics of Classes
classes-and-objects
类的对象去操作成员会更加的安全
类的成员函数在类内声明时,默认是inline函数
所以简单的函数在类内实现,复杂函数在类外实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
class Student {
private:
char name[4];
int born;
bool male;
public:
//类内实现,默认inline
void setName(cont cahr s) {
strcpy(name,s,sizeof(name))
}
void setGender();
void printInfo();
};
inline void Student:::setGender(bool isMale) {
male = isMale;
}
void Student::printInfo() {//不是inline函数
cout << name << endl ;
//...
}
|
Constructors-and-Destructors
构造函数与析构函数
构造函数可以有很多个,析构函数只能有一个
构造函数Constructors
1
2
|
struct in C:alloca te memory
class in C++:allocate memory&invoke a constructor
|
构造函数的用途是对 对象里面的数据 进行初始化
如果一个类不定义构造函数,编译器会默认生成一个默认构造函数
定义构造函数需要定义在public里面
每个new出来的对象,都会调用构造函数进行初始化
析构函数Destructors
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class Student {
public:
//...
Student() {
name = new char[1024]{0};
}
//...
~Student() {
delete [] name;
}
}
|
this-Pointer
对于类而言,函数的指令只有一份
All methods in a function have a this-pointer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
void setBorn(int b) {
born=b;
}
void setBorn(int b) {
this->born=b;
}
void setBorn(int born) {
this->born=born;//this指针不可省略,用来对参数进行区分
}
|
const-and-static-Members
const Members
常量成员变量不能被修改,常量成员函数不能去修改成员变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
class Student {
private:
const int BMI=24;
public:
int getBorn() const {
//born ++ ;//error
return born;
}
}
|
static Members
静态成员变量和静态成员函数并不绑定在某一个实例上
类的静态变量属于类,不属于实例化的对象
静态函数不能访问实例成员,也不能修改非静态数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
class Student {
public:
int born ;
static int stu_num ;//仅仅是声明
//inline static int stu_num = 0 ;//C++17标准,不需要外部定义
int getBorn() const {
//born ++ ;//error
return born;
}
static int getNum() {
return stu_num;
}
}
int Student::stunum = 1 ;//外部定义
|
Advances in Classes
Operator-overloading
运算符重载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
class complex {
public:
complex();//默认构造函数
complex(double,double);//初始化构造函数
complex(double);//强制转换构造函数
//*****************************************************//
//下面是二选一
complex operator + (const complex&);//运算符重载成员函数实现
complex operator - (const complex&);//运算符重载成员函数实现
friend complex operator + (complex&,complex&);//友元函数实现
friend complex operator - (complex&,complex&);//友元函数实现
//重载+=符号
complex & operator+=(const complex& comp1) {
this->real += comp1.real;
this->imag += comp1.imag;
return *this;
}
//****************************************************//
friend std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& , complex&);//istream类>>运算符重载
friend std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& , complex&);//ostream类<<运算符重载
private:
double real , imag ;
};
|
需要注意运算符重载是有方向的
1
2
3
4
|
complex comp1(1.0,1.0);
complex comp2(2.0,2.0);
comp1 += comp2;
//comp1.operator+=(comp2);
|
Friend-Functions
友元函数的声明在类内,能访问类的私有变量和私有函数,但是它不是类的成员,是一个特殊的函数
友元函数的定义可以在类内紧跟声明,也可以在类外
Operator << 也能被重载,一般采用友元函数形式重载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
//返回类型是输入输出流的引用
friend std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& , complex&);//istream类>>运算符重载
friend std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& , complex&);//ostream类<<运算符重载
/**************************************************/
friend std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& os, complex& comp) {
os<<comp.real<<"+"<<comp.imag;
return os ;//一定要返回os,为了能够链式调用
}
|
输入输出流的返回一定是输入输出流的引用,为了能够链式调用
user-defined-type-conversion
类转基本数据类型,运算符重载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
//implicit conversion
operator int() const {//允许隐式转换
return int(this->real) ;
}
//只允许显式转换
explicit operator float() const {
return float(this->real);
}
|
基本类型转类,可以利用构造函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
complex(int m):real(m),imag(0) {}
complex& operator=(int m) {
this->real = m ;
this ->imag = 0 ;
return *this ;
}
//上面是构造函数,在类内
//调用
complex comp1 = 100 ;//就会自动调用构造函数
//初始化 执行的是构造函数
comp1 = 10 ;//此处才是赋值运算符,赋值操作
comp1 = complex(20);//此处是构造函数
|
Increment
有前置(++i)和后置(i++)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
//都是类的成员函数
//prefix increment
complex& operator++() {//前置
this->real ++ ;
return *this ;
}
//postfix increment
complex operator++(int) {//后置,参数列表里面放int 主要是为了做区分
//需要保存旧值用来返回
complex old = *this ;//keep the old value
operator++();//prefix increment
return old ;
}
|
Dynamic-Memory-Management-in-Classes
Some-default-operations
Default-Constructors
默认构造函数
如果一个类没有任何构造函数,编译器就会生成一个空的构造函数,如果给类定义了构造函数,编译器就不会生成默认构造函数
需要避免歧义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
complex() {
cout << "man"<<endl ;
}
complex(int n=0) {
cout << "MAN" << endl ;
}
//此时就会有歧义,编译器奴知道执行哪一个
|
Implicitly-defined-Destructor
隐式定义的析构函数,没有显式定义析构函数,编译器会去定义一个空的析构函数
Default-Copy-Constructors
大疆C++一面:C++什么时候生成默认拷贝构造函数?
拷贝构造函数的参数必须是const引用(避免无限递归调用)
拷贝构造函数定义如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
complex::complex(complex & comp1) {
//...
}
complex comp(1.0,1.0);
complex comp_copy = comp;//copy constructor
complex comp_kobe(comp);//copy constructor
|
默认拷贝构造函数,如果用户没有显式定义,编译器会默认生成一个空的拷贝构造函数,该默认构造函数会将对象里面的所有非静态成员全部拷贝一遍
可以使用下面的=delete来让编译器不去提供默认的copy-constructors
1
|
complex(const complex&)=delete;
|
Default-Copy-Assignment
Assignment operators:=,+=,-=
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
complex& complex::operator=(complex & comp) {
//...
}
complex comp(1.0,1.0);
complex comp_man = comp;//copy constructor拷贝构造函数
comp_man = comp;//copy assignment
|
Default-Copy-Assignment
如果用户没有定义Copy-Assignment,编译器会自动生成一个默认的Copy-Assignment
该默认函数会将对象所有的非静态成员变量全部拷贝一遍
可以使用下面的=delete来让编译器不去提供默认的copy-assignment
1
|
complex & operator= (const complex&)=delete;
|
Copy-Assignment
注意赋值运算符在内存管理上的细节
- 避免自赋值
- 赋值前先回收,避免内存泄漏
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class ClassA {
public:
ClassA() {}
ClassA(const char* pszInputStr) {
pszTestStr = new char[strlen(pszInputStr) + 1];
strncpy(pszTestStr, pszInputStr, strlen(pszInputStr) + 1);
}
virtual ~ClassA() {
delete pszTestStr;
}
// 赋值运算符重载函数
ClassA& operator=(const ClassA& cls) {
// 避免自赋值
if (this != &cls) {
// 避免内存泄露
if (pszTestStr != NULL) {
delete pszTestStr;
pszTestStr = NULL;
}
pszTestStr = new char[strlen(cls.pszTestStr) + 1];
strncpy(pszTestStr, cls.pszTestStr, strlen(cls.pszTestStr) + 1);
}
return *this;
}
public:
char* pszTestStr;
};
int main() {
ClassA obj1("liitdar");
ClassA obj2;
obj2 = obj1;
cout << "obj2.pszTestStr is: " << obj2.pszTestStr << endl;
return 0;
}
|
An-Example-with-Dynamic-Memory
注意深拷贝与浅拷贝的问题,导致重复释放同一块内存
这种错误最容易由 默认拷贝构造函数 和 默认赋值运算符重载 导致
Hard-Copy
每次创建和赋值的时候都去重新申请内存
缺点在于如果每次申请的内存较大会很耗时
Soft-Copy
如果是赋值操作,或者 拷贝构造,可以让两个变量共享同一块内存,同时用过一个变量去记录该块内存的引用数量
Smart-Pointers
使用智能指针的话,可以只管申请,不管释放,系统会自动帮你释放,释放delete会调用对应的析构函数
std::shared_ptr
定义
1
2
3
|
std::shared_ptr<数据类型> man(new 数据类型(参数列表));//参数列表是构造函数的参数列表
std::shared_ptr<string> man(new string("MAN"));
auto MAN = std::make_shared<int>(119);
|
多个指针指向的是同一个对象,共享
std::unique_ptr
指针指向一个对象后,就不允许分享
1
2
3
4
5
|
std::unique_ptr<string> man(new string("MAN"));
auto MAN = std::make_unique<int>(119);//C++17标准
std::unique_ptr<string> m3 = std::move(man);//移动过去后,man成了空指针
std::unique_ptr<int> m4 = MAN ;//error
|
How-to-Understand-Smart-Pointers
智能指针的定义,是指针的同时还是一个对象
1
2
3
|
template<class T>class shared_ptr;
template<class T,class Deleter=std::default_delete<T>>class unique_ptr;
|
Class-Inheritance
Improve-your-source-code
- 在赋值操作上,很多时候一个一个赋值不如
memcopy直接将内存的内容复制过去效率高
- 二维数组最好用一维数组去表达,因为这样不用多次去申请一维的内存,多次申请的一维数据不保证连续,会降低读取速率
- 一个函数,一定要去检查函数的参数是否有效
- 注意头文件重复包含的问题
- 注意内存对齐
- 函数的输入参数,不需要修改的加
const关键字
Derived-class
Base class(parent),Derived class(child)
一个是基类(父类),一个是派生类(子类)
可以多层继承和多个继承
构造函数与析构函数在子类中的执行
构造函数
子类的构造函数执行的第一刻,父类的构造函数先执行
下面子类的构造函数执行顺序:Base的构造函数->MAN的赋值->最后是子类构造函数内部
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
class Derived :public base {
public :
int MAN ;
Derived(int man):Base(man-1,man-2),MAN(man) {
//...
}
};
|
析构函数
子类的析构函数会先执行子类的析构函数,再执行父类的构造函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class Derived :public base {
public :
int MAN ;
Derived(int man):Base(man-1,man-2),MAN(man) {
//...
}
~Derived() {
//...
}
};
|
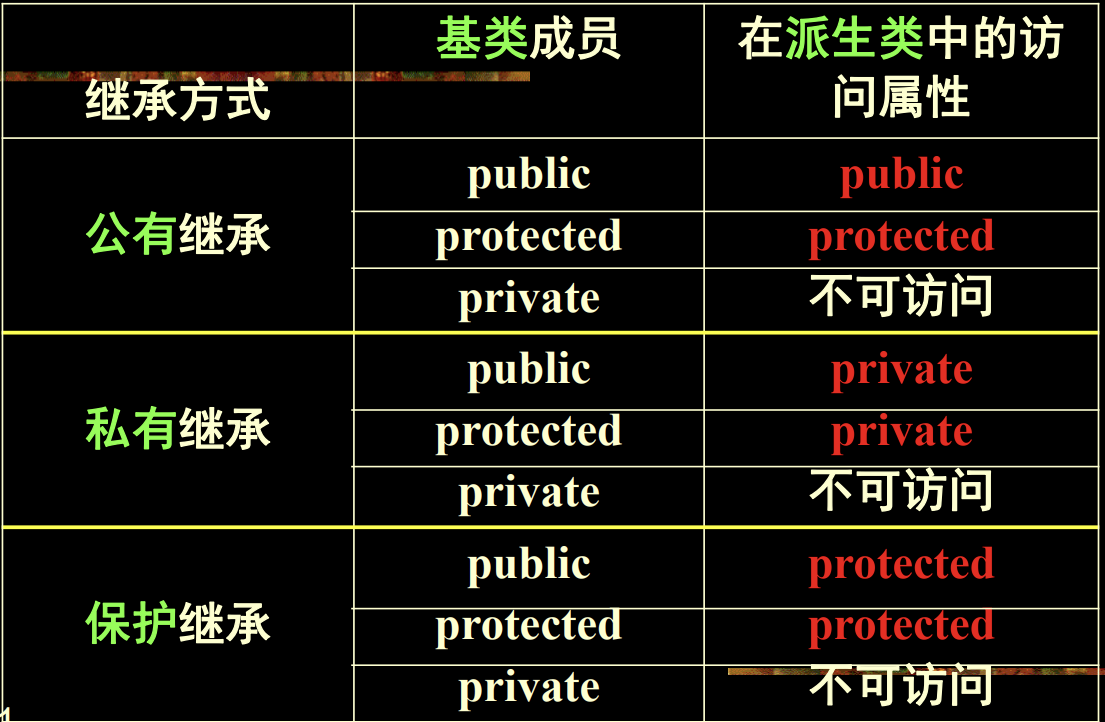
Acess-Control
访问控制
private只能类内访问,protected可以在类内和子类里面访问
关于继承方式:有三种继承方式,public,protected,private
Virtual-Functions
虚函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
class A{
protected:
int x;
public:
A(){
x =1000;
}
virtual void print(){ //虚函数
cout << "x=" << x << endl ;
}
};
class B:public A{
int y;
public:
B() {
y=2000;
}
void print() { //派生虚函数
cout << "y=" << y << endl ;
}
};
class C:public A{
int z;
public:
C(){
z=3000;
}
void print(){ //派生虚函数
cout << "z=" << z << endl ;
}
};
void main(void ) {
A a, *pa;
B b;
C c;
a.print(); b.print(); c.print(); //以上为静态关联
pa=&a; pa->print(); //调用类A的虚函数
pa=&b; pa->print(); //调用类B的虚函数
pa=&c; pa->print();//调用类C的虚函数
}
|
虚函数与非虚函数的绑定不同,常规函数都是静态绑定,虚函数是动态绑定
有虚函数时,此类定义的对象会有一个隐含的成员变量,该隐含变量会指向一个函数表
对于纯虚函数,在类内定义
1
|
virtual void print() = 0;
|
来告诉编译器这是一个纯虚函数,拥有纯虚函数的类就不能创建对象
另外,析构函数也是一个虚函数
Inheritance-and-dynamic-memory-allocation
如果一个子类只有基类有动态内存申请,就不用考虑子类,只需要解决基类的问题,自定义写 构造函数,赋值运算符重载,拷贝构造函数
如果子类有动态内存申请,解决方案一样,重新把 构造函数,拷贝构造函数,赋值运算符重载 定义即可
下面用伪代码展示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
class MyMap:public MyString {
private:
char *keyname;
public:
MyMap(const char *key , const char *value) {//会自动先调用基类的构造函数,此处不需要向基类构造函数传递参数
//...,为新的指针变量动态申请内存
}
//析构函数将子类的指针申请的动态内存释放掉
MyMap(const MyMap &mm):MyString(mm.buf_len,mm.characters) {//给基类的构造函数传递参数,调用基类的构造函数去申请内存
//allocate memory for keyname
//and hard copy from mm to *this
}
MyMap & operator=(const MyMap &mm) {
MyString::operator=(Mys(mm));//调用基类的
//allocate memory for keyname
//and hard copy from mm to *this
return *this;
}
};
|
Class-Templates-and-Std-Library
模板十分实用,前面有函数模板,此处是类模板
函数模板回顾
函数模板生成的函数是模板函数,模板函数是函数模板被实例化以后生成的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
template <typename T>
T sum(T x , T y ) {
cout <<"The input type is " << typeid(T).name() << endl ;
return x+y ;
}
template double sum<double>(double,double);//实例化
template char sum<>(char,char);
template int sum(int,int);
|
类模板和模板类也是类似的
class-template
类模板的定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
template<typename T>
class Mat {
uint16_t rows ;
uint16_t clos ;
T* data ;
public :
Mat(uint16_t rows,uint16_t cols):rows(rows),cols(cols) {
data = new T[rows*cols]{};
}
~Mat() {
delete [] data;
}
T getElement(uint16_t r , uint16_t c);//函数模板,类内声明
bool setElement(uint16_t r , uint16_t c , T value);//函数模板,类内声明
};
//类内函数模板的类外定义
template <typename T>
T Mat<T>::getElement(uint16_t r , uint16_t c) {//getElement是Mat<T>的成员函数
if( r >= this->rows || c >= this->cols ) {
cout << "getElement():Indices are out of range" << endl ;
return 0 ;
}
return data[this->cols*r+c];
}
template <typename T>
T Mat<T>::setElement(uint16_t r , uint16_t c , T value) {
if( r >= this->rows || c >= this->cols ) {
cout << "setElement():Indices are out of range" << endl ;
return false ;
}
data[this->cols*r+c]=value;
return true ;
}
//显式实例化
template class Mat<int>;
|
模板的参数
declare a template
1
|
template <parameter-list> declaration
|
The parameters can be
type template parameters(例如int,float 类型) `templaate- template parameters(模板类型做为参数)`
non-type template parameters(定值,float,int类型的定值,例如1.0f,值参数)
Template-Non-Type-Parameters
模板的非类型参数
此处相当于在编译时就要确定矩阵有多少行多少列,而不是动态申请
因为不需要动态申请,也就没有必要析构的时候删除
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
template<typename T,uint16_t rows,uint16_t cols>
class Mat {
T data[rows][cols];
public:
Mat() {}
T getElement(uint16_t rows,uint16_t cols);
bool setElement(uint16_t r , uint16_t c , T value);
};
|
1
2
3
4
|
Mat<int> vec1(3,3);//会在构造函数内部动态申请内存
Mat<int,3,3> vec2;//编译时就确定
typedef Mat<int,2,2> Mat22i;//简化
|
另外补充,静态数组的默认拷贝构造,是一个一个值复制过去,不会有内存管理问题
模板类是可以相互继承的
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//继承模板类,需要template<typename _Tp, int cn>
template<typename _Tp, int cn>class Vec:public Matx<_Tp,cn,1> {
public;
typedef _Tp value_type;
};
|
Class-template-specialization
类模板的特化
一个MyVector的类模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
template<typename T>
class MyVector {
uint16_t length ;
T *data ;
public :
MyVector(uint16_t length):length(length) {//构造函数
data = new T[length]{};//所有元素初始化为0
}
~MyVector() {
delete [] data ;
}
MyVector(const MyVector&)=delete;//删除拷贝构造函数
MyVector& operator=(const MyVector&)=delete;
T getElement(uint16_t index);
bool setElement(uint16_t index , T value);
};
template<typename T>
T MyVector<T>::getElement(uint16_t index) {
//...
}
|
bool类型变量是一个字节,因为内存管理删除申请的最小单位是一个字节
现在对于上述模板想使用bool,又想更加压缩内存,可以将bool类型的模板特化,特殊情况特殊处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
template<>
class MyVector <bool> {
uint16_t length ;
unsigned char *data ;
public :
MyVector(uint16_t length):length(length) {//构造函数
int num_bytes = (length-1)/8+1;
data = new unsigned char [num_bytes]{};//所有元素初始化为0
}
~MyVector() {
delete [] data ;
}
MyVector(const MyVector&)=delete;//删除拷贝构造函数
MyVector& operator=(const MyVector&)=delete;
bool getElement(uint16_t index);
bool setElement(uint16_t index , bool value);
};
bool MyVector<bool>::getElement(uint16_t index) {
//...
}
|
std-classes
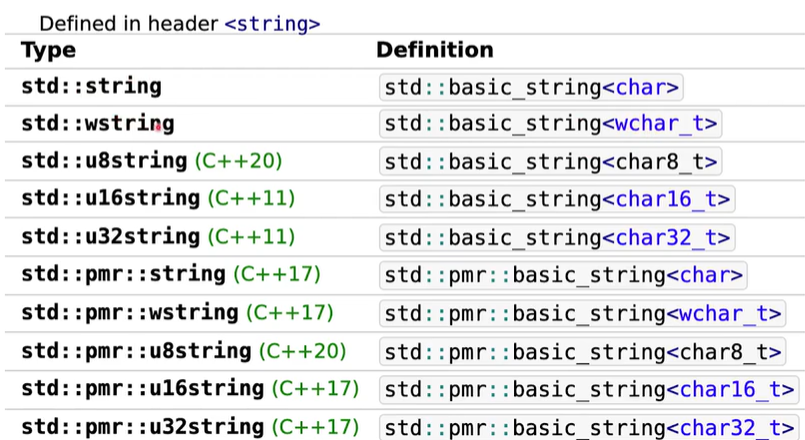
std::string
array
1
2
3
|
template<class T,std::size_t N>struct array;
std::array<int,3>a = {1,2,3};
|
others


Error-Handling
Standard-Output-Stream-and-Standard-Error-Stream
标准输出流与标准错误流
C&C++的输出流与错误流
 标准输出流的内容可以通过管道输出到其他文件,而标准错误流不会
标准输出流的内容可以通过管道输出到其他文件,而标准错误流不会
重定向
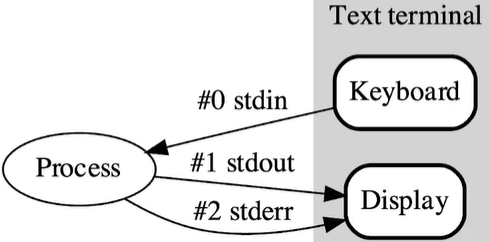
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
./program | less
./program > output.log 将stdout输出到output.log文件,如果文件已存在就销毁再创建,内容覆盖
./program 1> output.log 将stdout输出到output.log文件
./program >> output.log 将stdout输出到output.log文件,如果没有则创建,有内容则加到已有内容后面
./program 2> error.log 将stderr输出到error.log文件
|
由此可以看出关于日志的重要性,以及日志是什么
assert
在编译过程中,方便debug的工具
Exceptions
catch,try与throw
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
float ratio( float a , float b ) {
if(...)
throw 1;
if(...)
throw 2;
return a+b;
}
try{
z = ratio(x,y);
}
catch(int eid) {
//...
}
|
throw相当于扔出一个异常,再函数调用中一级一级往上,如果有catch,就进入对应的catch的处理,否则若返回到main函数中仍没有catch,程序就会被杀死
1
2
3
4
|
catch(...) { //表示所有异常都能接住
std::cerr<<"Unrecognized Exception"<<std::endl;
//...
}
|
throw可以扔一个类,std标准可有提供std::exception的类
Nested-Classes-and-RTTI
Friend-Classes
复习一下友元函数,注意有顺序问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class MyVector {
//...
public:
friend MyVector operator(int m , const MyVector& v);
};
MyVector operator+(int m , const MyVector &v ) {
MyVector v_trmp ;
//...
return v_temp ;
}
|
友元类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
class Sniper {
private:
int bullets;
public:
Sniper(int bullets=0):bullets(bullets){}
friend class Supplier;//仅仅是声明
}
|
Friend-Member-Functions
可以用来实现最小授权,另一个类的某一个成员函数可以访问
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
class Supplier;//先声明
class Sniper {
private:
int bullets;
public:
Sniper(int bullets=0):bullets(bullets){}
friend bool Supplier::provider(Sniper &);
}
class Supplier{
//...
}
|
注意顺序问题以及先声明再实现的处理方法
Nested-Types
内部类型,此处的enum DataTYpe即是内部类型,作用是这个枚举类型仅Mat类能用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
class Mat {
public:
enum DataType {
TYPE8U,
TYPE8S,
TYPE32F,
TYPE64F
};
private:
DataType type ;
void* data ;
public:
Mat(DataType type):type(type),data(NULL){}
DataType getType() const { return type ;}
};
|
Nested-Classes
与内部类型的类似,不用过多赘述,著需要注意在使用时加上前缀
1
|
Storage::Fruit apple("apple",100);
|
Runtime-Type-Identification(RTTI)
运行时的类型鉴别
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class Person;
class Student: pubic Person;//student类对person类进行了拓展
Person person("Yu");
Student student("MAN","20210212");
Person *pp = &student ;//ok
Student *ps = (Student*)&person;//danger
//从内存管理角度去理解会很简单,本质还是访问内存越界的问题
cout << ps->getInfo() << endl ;//可能会访问不该访问的内存
|
但是如果getInfo是virtual虚函数,则会有动态绑定,不会出现访问越界的问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
dynamic_cast operator:conversion of polymorphic types.
polymorphic types(多态类型)
typeid operator:Identify the exact type of an object.
|
可以用typeid()操作符来获取类的名称
1
2
|
if( typeid(std::string)==typeid(s) )
cout << "s is a std::string object." << endl ;
|
使用dynamic_cast转换(仅多态类型使用)
多态类型的类里面需要有virtual
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
class Person;
class Student: pubic Person;//student类对person类进行了拓展
Person person("Yu");
Student student("MAN","20210212");
Person *pp = NULL ;
Student *ps = NULL ;
ps = dynamic_cast<Student*>(&person);//不会进行转换,转换失败,ps=NULL,更安全
pp = dynamic_cast<Person*>(&student);
|
More-Type-Cast-Operations
const_cast:Type cast for const or volatile value .
static_cast:如果两类型能够隐式转换,则发生转换,否则不能转
1
2
3
|
Base *pB = static_cast<Base*>(derived);//valid
Derived *pD = static_cast<Derived*>(base);//valid
UnRelated *pU = static_cast<UnRelated*>(base);//invalid
|
reinterpret_cast:Converts between types by reinterpreting the underlying bit pattern.
1
2
3
|
int i = 18;
float *p1 = reinterpret_cast<float *>(i);//static_cast will fail
int *p2 = reinterpret_cast<int *>(p1);
|
Code-Optimization
Register-and-Cache
三级,Register,Cache,Memory
一般通过Latency延迟,Bandwidth带宽这两个指标来衡量
在访问内存中连续数据的情况下,访问速度会更快
现代多核的CPU在缓冲区的设置上会更复杂,会分为专门存放指令的区域和专门存放数据的区域,同时多核会有共享的缓存区
Locality-of-Reference
局部性主要有时间局部性和空间局部性,局部性是观察程序的运行得出的
时间局部性是指同一块内存在一两个指令周期后很有可能会被再次访问
空间局部性是指被访问的一块内存,其周围也会很有可能被访问
计算CPU优化效率
Peak_FLOPS=2*Frequency*cores*每周期发送的指令*(指令宽度/数据宽度)
3GHz,24核,每周期发送2指令,指令宽度512比特
假设算的是double(64比特)
FLOPS=2*3G*24*2*(512/64)
有效floating op计算
Matrix A是m*k,Matrix B是k*n,Matrix C是m*n
Effected floating op = 2*m*k*n
衡量优化效率
Efficiency=Eddected_Performance/Peak_Performance
个人的补充与总结
关于Include
1
2
|
include <>//从编译器指定的路径去找
include ""//从编译器指定的路径去找以及当前.cpp文件所在目录去找
|
关于类
关于模板
c++模板编程应该把实现放在头文件中吗,这样写会不会让头文件变得很难看? - 知乎
借用其中的一个回答
理论上,模板函数的实现应该放在头文件里,这是因为 C++ 继承了 C 语言先分离编译最后链接的传统,而模板的实例化在编译期,所以必须要让编译器看到函数的实现,才能实例化
这里从原理上来看就知道模板的声明和定义(实现)应该都放在头文件中了,不然在编译期引用了模板实例化的源文件会无法正常编译,也就是无法正常生成实例化的模板函数,类模板同理
详解如下
C++中模板以及模板实例化都放在头文件_模板特化能放到cpp文件吗-CSDN博客
关于全特化,函数模板的特化版本本质上是一个具体的函数(不再是模板),但由于它与通用模板存在关联,实践中几乎都放在头文件中
类模板特例化的同样规则,类模板的全特化和部分特化也建议放在头文件中
原因如下
- 避免隐式实例化冲突
当编译器处理模板实例化时,如果在某个编译单元中看不到特化版本的声明,会自动实例化通用模板。若此时其他编译单元存在特化版本的实现,会导致链接时出现 “多重定义” 错误
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
// 头文件(func.h)
template<typename T>
void print(T value) { // 通用模板
std::cout << value;
}
// 特化版本放在头文件,确保所有使用处可见
template<>
void print<const char*>(const char* str) {
std::cout << "String: " << str;
}
|
- 符合模板使用习惯
模板(包括特化)的使用者通常会通过头文件获取完整定义,无需关心实现文件的链接细节。将特化放在头文件中,能让代码结构更清晰,减少外部依赖
类模板和函数模板的例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
// 1. 基本函数模板
template<typename T>
T max(T a, T b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
// 2. 函数模板特化(针对特定类型)
template<>
const char* max<const char*>(const char* a, const char* b) {
return strcmp(a, b) > 0 ? a : b;
}
// 使用
int i = max(3, 5); // 隐式实例化int版本
const char* s = max("apple", "banana"); // 调用特化版本
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
// 1. 基本类模板
template<typename T, int Size>
class Array {
private:
T data[Size];
public:
Array() {}
T& operator[](int index) {
return data[index];
}
int getSize() const { return Size; }
};
// 2. 类模板特化(针对bool类型优化)
template<int Size>
class Array<bool, Size> {
private:
unsigned char data[(Size + 7) / 8]; // 位压缩存储
public:
bool get(int index) const {
return (data[index / 8] >> (index % 8)) & 1;
}
};
// 使用
Array<int, 10> intArray; // 实例化int类型数组
Array<bool, 100> boolArray; // 使用特化版本
|



 申请内存
申请内存 引用创建的时候一定要初始化
引用创建的时候一定要初始化





 标准输出流的内容可以通过管道输出到其他文件,而标准错误流不会
标准输出流的内容可以通过管道输出到其他文件,而标准错误流不会